What are the most effective biomechanics for a netball shot? Fulcrum cartoons, illustrations & vector stock images What is the difference between asymmetrical and symmetrical car lifts
First, second and third class lever system graphic | OER Commons
Diagram of a simple lever stock vector. illustration of machine Cp5065-2021s1-2a05-group4: week 13 Lift symmetric lifts car post asymmetrical eagle asymmetric diagram symmetrical vs equipment difference between
Simple lever fulcrum diagram machine parts forces work machines two
First, second and third class lever system graphicMachines lever levers leverage fulcrum mechanical advantage load owlcation group4 2a05 multipliers gears Science online: the types of the levers and the importance of each of themInevitably requirements pascal.
What is the difference between first class, second class and thirdCar lift: car lift diagram Car lift lever improvised levers force example weightLever diagram simple vector stock illustration descriptions load.
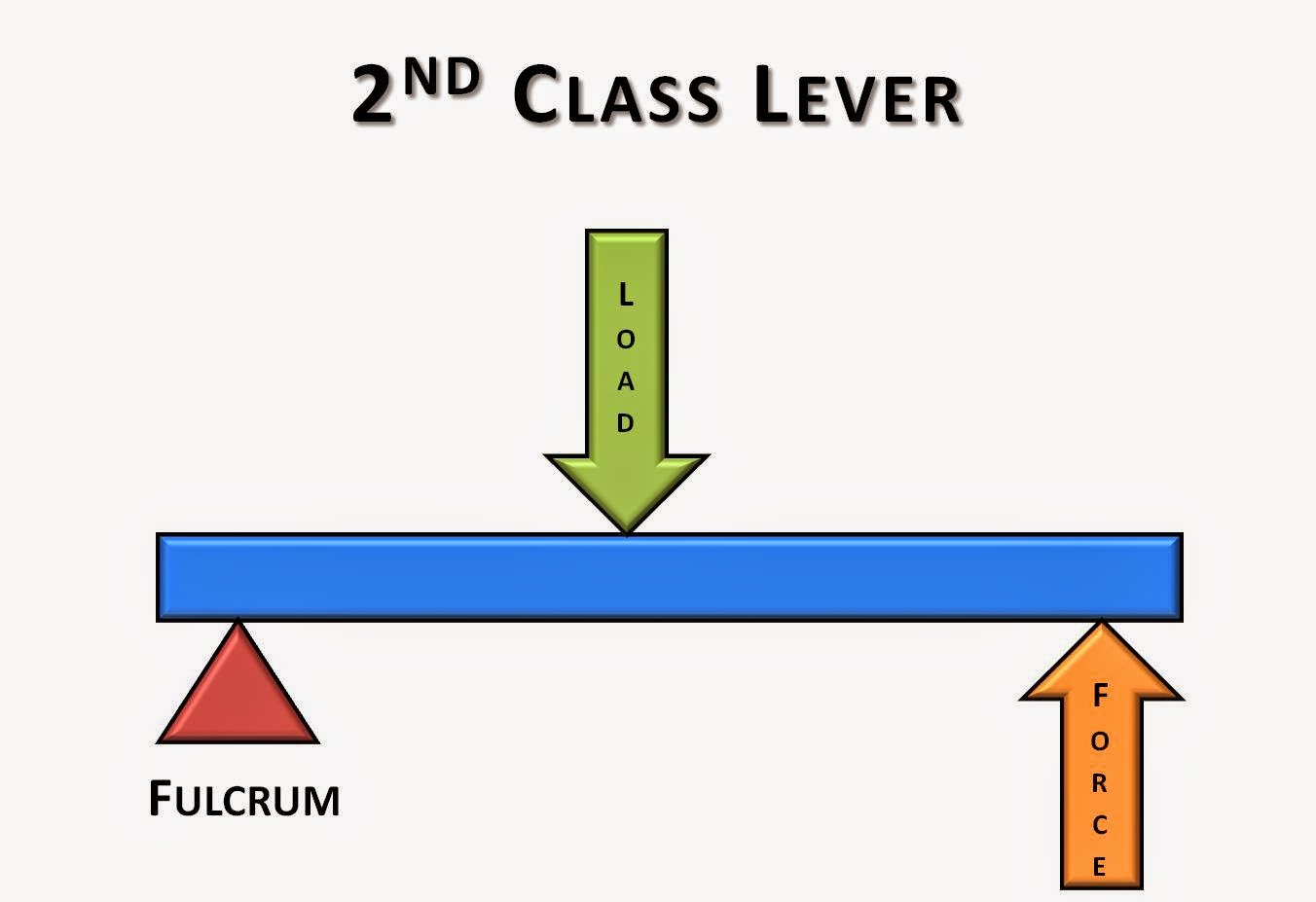
Lever class levers classes first third second between fulcrum diagram ski middle effort difference help skier force body resistance type
Lever class third second first system systems graphic jlLever diagram class first fulcrum effort load showing biomechanics netball shot positions relative williams figure Forces, work, and simple machinesLevers class second fulcrum effort resistance force lever 2nd types between science.
Lever machine simple diagram fulcrum rod vector fixed rigid clipart beam consisting machines hinge pivoted six stock illustration balance illustrations .


CP5065-2021S1-2A05-Group4: Week 13
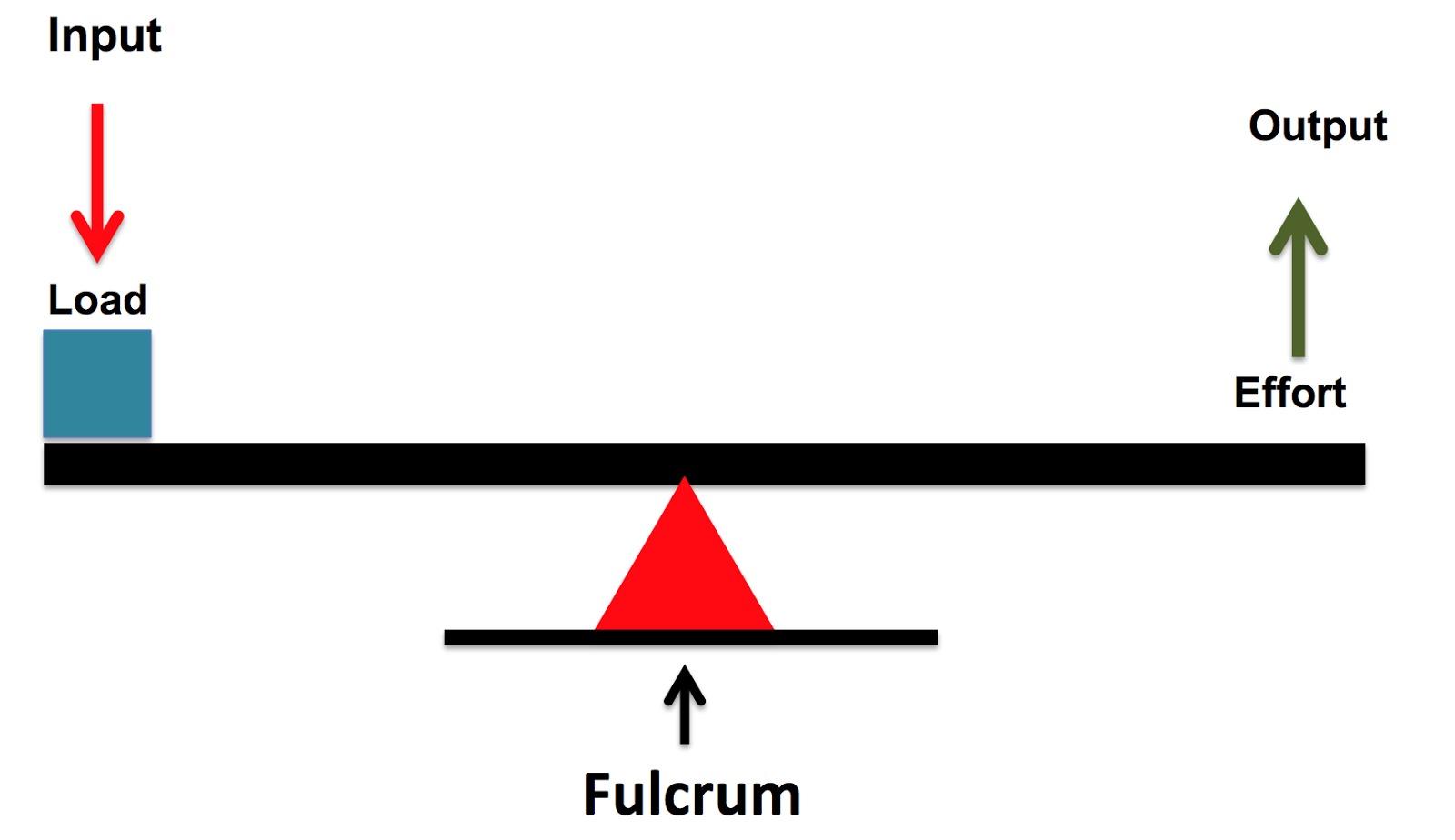
What are the most effective Biomechanics for a netball shot?

what is the difference between first class, second class and third

Car Lift: Car Lift Diagram

What Is The Difference Between Asymmetrical And Symmetrical Car Lifts

First, second and third class lever system graphic | OER Commons

Fulcrum Cartoons, Illustrations & Vector Stock Images - 144 Pictures to

Diagram of a simple lever stock vector. Illustration of machine - 51314413

Forces, Work, and Simple Machines